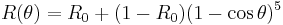Schlick's approximation
In 3D computer graphics, Schlick's approximation is a formula for approximating the bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) of metallic surfaces. It was proposed by Christophe Schlick to approximate the contributions of Fresnel terms in the specular reflection of light from conducting surfaces.
According to Schlick's model, the specular reflection coefficient R is given by
where 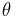 is half the angle between the incoming and outgoing light directions, and
is half the angle between the incoming and outgoing light directions, and 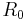 is the reflectance at normal incidence (i.e., the value of the Fresnel term when
is the reflectance at normal incidence (i.e., the value of the Fresnel term when 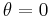 ).
).
See also
References
- Schlick, C. (1994). "An Inexpensive BRDF Model for Physically-based Rendering". Computer Graphics Forum 13 (3): 233. doi:10.1111/1467-8659.1330233.